Ultrasound imaging is a term that almost everyone has heard at one point or another. There are many reasons why diagnostic ultrasound is one of the most common testing processes done in the medical field.
Ultrasound scanning is so common that you will find a diagnostic ultrasound machine in every medical testing facility. However, while people know what an ultrasound examination is, not many have an in-depth understanding of how it works.
What is an ultrasound machine, and how does it work? In this article, we will cover the basics of ultrasound technology, how it works, and the different types of ultrasound imaging devices available.
What is Medical Ultrasound Imaging?
It is a medical imaging method that uses sound waves on a body’s internal organs for testing, diagnostic, or therapeutic reasons. The sound waves travel through the body and are converted into an ultrasound image showing the condition and boundaries of fluid and soft tissue and internal organs in the body. This allows medical staff to diagnose problems and decide on treatment programs.
Using medical ultrasound imaging allows doctors to diagnose problems with internal organs and sources of inflammation or pain in the body.
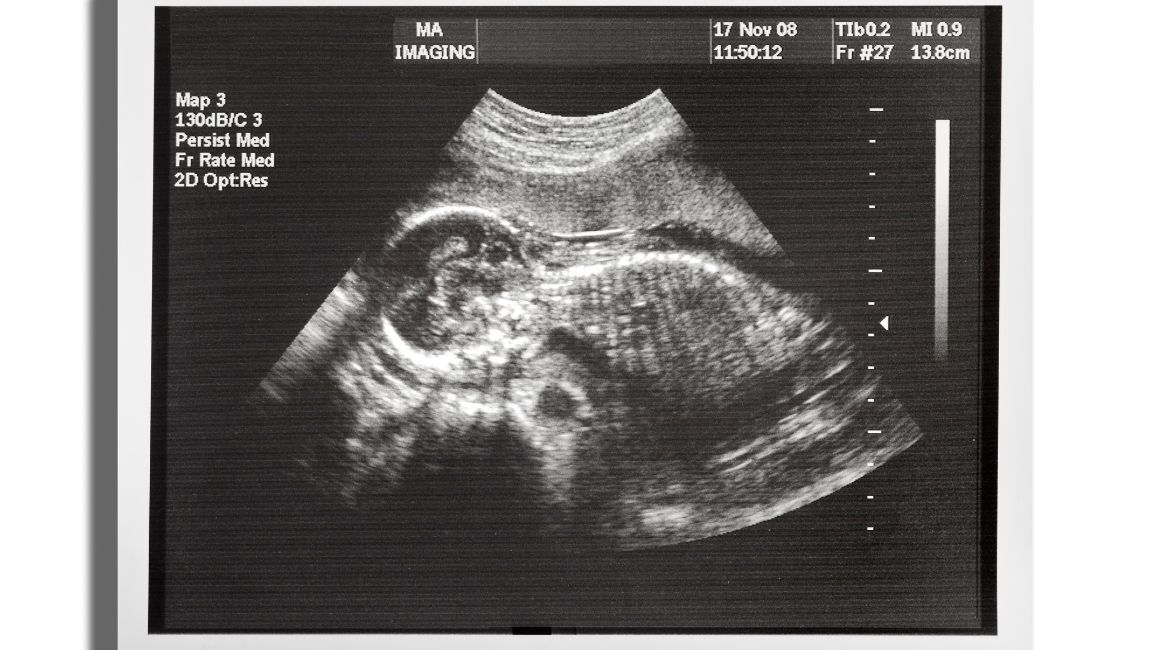
Not only that, but ultrasound imaging is the most common testing method used on pregnant women to monitor the growth of a fetus inside the body.
This imaging technique uses ultrasound waves, which are very high-frequency sound waves. These sound waves cannot be heard or differentiated by human ears.
What is the difference between Ultrasound and Sonography?
Many people hear the term ‘sonography’ and consider it the same as ultrasound. While the two are similar, there are differences that you should be aware of.
As we mentioned earlier, the ultrasound process can be diagnostic or therapeutic. When it is diagnostic, it is used as an imaging method. When it is therapeutic, no imaging is generated. Typical therapeutic applications involve delivering deep heat to soft tissue areas.
Sonography is the term used for the imaging application of ultrasound technology. When used for diagnostic purposes and generating a picture, the method is called sonography.
The image created is called a sonograph, and the technician conducting the ultrasound examination is called a sonographer.
What is the difference between Ultrasound and CT Scan?
A Computerized Tomography (CT) scan is another common medical imaging procedure used to identify ailments inside the body. However, this is quite different from ultrasound scan procedures.
CT scans utilize X-rays to generate a detailed image of the body’s internal organs. The X-ray tube rotates to capture images of different body sections and tissues.
Since CT scans use X-rays, the procedure is radioactive and potentially harmful to some extent. However, ultrasound scans produce no ionizing radiation exposure since they use sound waves instead.
A Short History of Ultrasound
While the concept of ultrasound waves was established more than 100 years ago, the use of this science in medicine was adopted after the Second World War. Some of the most memorable dates in the evolution of ultrasound technology are:
- In 1947, Austrian physician Karl Dussik, with his physicist brother Friederick, used ultrasound to create a visualization of cerebral ventricles. This was a breakthrough in medical ultrasound imaging.
- In 1949, George Ludwig utilized ultrasound imaging to analyze gallstones in soft tissue. This furthered the use of ultrasound waves for the accurate diagnosis of medical conditions.
- Ultrasound imaging found its commercial application in medicine in 1963 with Brightness Mode devices. These devices helped in forming a two-dimensional image of tissues and organs.
- In the ’80s, ultrasound scan machines incorporated the principles of the Doppler effect to create colour flow Doppler ultrasound which could visualize and measure blood flow through a blood vessel.
When was the ultrasound machine invented?
The first medical ultrasound machine was developed in Glasgow by obstetrician Ian Donald and an engineer, Tom Brown. It was first invented in 1956 and further improved till it was perfected around 1959.
How Does an Ultrasound Machine Work?
The working principle behind an ultrasound machine is similar to that of SONAR systems used in military and naval applications. Even bats use this principle to hunt their prey without relying on their sight.
So how does ultrasound work? Let’s examine how a typical ultrasound machine works.
An ultrasound machine uses high-frequency sound waves, emitting these waves toward the body. These waves penetrate the skin and bounce off the inner organs and tissues.
When they bounce and reflect, the reflected waves are recorded by the machine. The patterns of these reflections are used to generate visualizations of the inner organs and tissues of the body.
Now, you might be wondering how the waves penetrate some organs while reflecting off others. This phenomenon is decided by the wavelength/frequency of the sound wave used.
The frequency of ultrasound waves in medical applications is between 2 MHZ and 15 MHZ. The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength and the more attenuation. Therefore, reducing the frequency and absorption allows us to study body structures and other features.
In the same way, superficial body structures can be studied by increasing the frequency of the ultrasound machine.
Here are the frequencies used to examine different body parts:
- 2.5 MHZ: Present on the shortest frequency end of the ultrasound wave scale; this frequency is used for abdominal ultrasound to study the deep abdomen and for obstetric and gynecological applications.
- 3.5 MHZ: This frequency moves the study from deep to general areas of the abdomen, obstetric, and gynecological applications.
- 5 MHZ: This frequency is used to study the circulatory system, lymph nodes, pelvic areas, and breasts.
- 7.5 MHZ: This frequency studies the breasts and the thyroid glands.
- 10 MHZ: This frequency is used to study the breasts and thyroid, and analyze the superficial veins and masses. It also applies to analyzing the musculoskeletal system of the body.
- 15 MHZ: At the highest end of the frequency spectrum for medical imaging, this frequency also studies the musculoskeletal system and other superficial masses.
What is Inside an Ultrasound Machine?
Ultrasound scanning has evolved significantly over the past few decades. The machinery has been developed to become more compact, and the resulting imagery has become more detailed, high-quality, and vivid. Typical components of an ultrasound machine include:
Transducer
The transducer sends and receives the sound waves. If you have seen an ultrasound machine, the transducer is the small handheld probe that the technician uses. In early devices, sending and receiving these waves was done by two different units.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The Central Processing Unit is the brain behind an ultrasound machine. It coordinates the different signals emitted and received by the transducer, interpreting the electrical signals in the form of a visual image on the monitor.
Display
The display or monitor shows the image of what the transducer is scanning. This allows the doctor to analyze the image before creating their diagnosis. It also enables the technician to navigate to the exact area that requires ultrasound imaging.
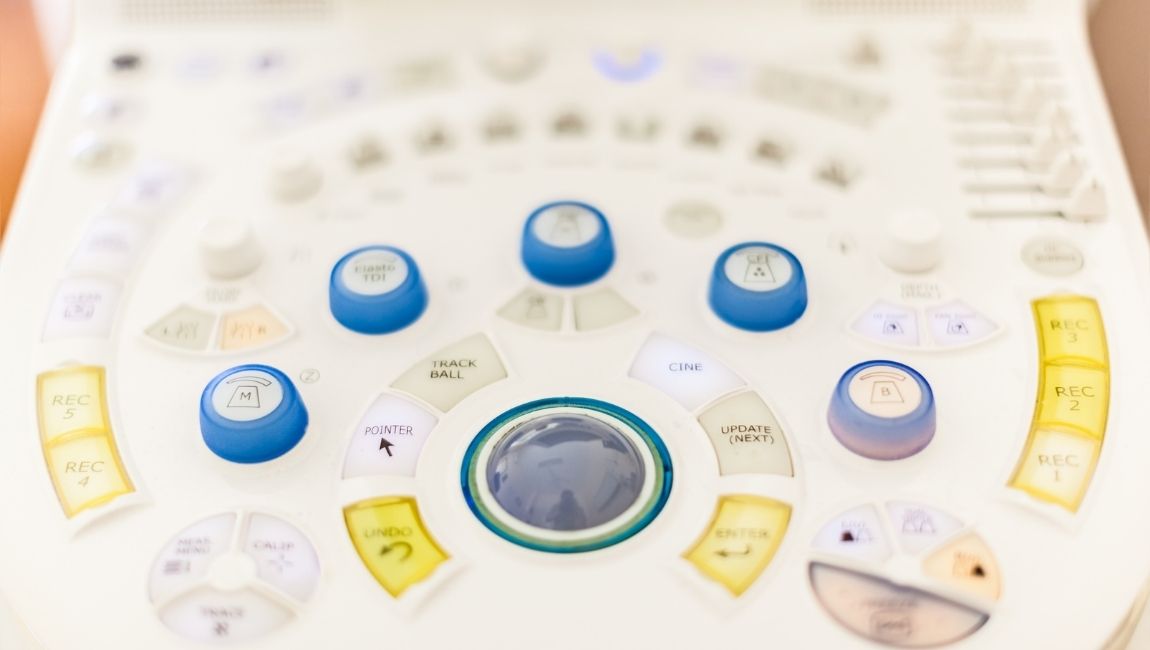
Control Knobs
Control knobs enable the technician to adjust the settings for ultrasound scans to get a clear picture on the display. Other functions include zooming the picture in and out.
Keyboard
Keyboards are used during ultrasound scans to enter patient data. Entering patient data allows every image to be saved correctly in the patient file. Storing patients’ ultrasounds with their data helps maintain accurate patient records on any digital medium.
Printer
The printer is used to print a hard copy of the ultrasound image. The hard copy can be used for examination by another doctor or saved in a patient’s file for use later. Hard copies of images are also given to expecting parents as a picture of their child.
What are the Different Types of Ultrasound Machines?
In the early stages of its development, ultrasound technology was limited to creating blurry 2-dimensional images of the area of interest. However, with modern technology, the results that can now be obtained are fascinating.
Modern ultrasound machines are of many types, but they can be divided into 2 main categories:
3D Ultrasound Imaging
Three dimensional (3D) ultrasound imaging machine captures different 2D images of the area of interest by the movement of the probe. These images obtained by ultrasound transducers are then superimposed by specialized software built into the machine, forming a 3D model of the tissue.
3D ultrasound imaging is often utilized to detect benign tumors and cancer in the early stages. Common areas for detection include the breasts, colon, prostate, and rectum.
3D imaging is also used to study fetal development and detect abnormalities in its growth, such as disproportionate limbs. It can even measure the blood flow in fetal blood vessels.
Doppler Ultrasound
The Doppler effect is based on sound waves and their echo reflected from moving objects. When ultrasound machines incorporate this principle, the process becomes Doppler ultrasound.
Doppler ultrasound is generally restricted to moving particles. Therefore, it is applied for studying the blood flow through the heart and the blood vessels in the body.
What are the Uses of Ultrasound in Medicine?
There are dozens of medical applications for ultrasound machines. Here is a list of various cases where the technology is used to examine the body:
Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- In the field of OBGYN, medical ultrasound is used to study the different stages of pregnancy. It can determine the size of the fetus along with fetal development and the due date.
- Imaging depicts the number of fetuses, thereby predicting the possibility of multiple births. The doctors can also define the sex of the unborn baby.
- Ultrasound imaging can also provide information on problems in pregnancy, such as the baby being implanted in the fallopian tubes instead of the uterus.
- Even in the absence of pregnancy, ultrasound imaging is used to diagnose any probable tumors or cysts in the ovaries.
Urology
- Ultrasound is the most common method to diagnose kidney stones.
- It is also used to examine blood flow in the kidneys and diagnose other kidney ailments.
- Medical ultrasound imaging can help diagnose prostate cancer early and prevent cancerous growth.
Cardiology
- Cardiac ultrasound machines can detect if the heart is functioning healthily by checking the blood flow through the heart. Cardiac ultrasound can also help in identifying any abnormalities or heart conditions.
- If there are any blockages in the heart or the nearby arteries, they can be detected with ultrasound examinations.
- It is also used to monitor the blood flow through the heart and blood vessel health.
Biopsy and Probing
- Ultrasound-guided biopsies allow surgeons to guide the probes and tools used during a procedure.
- A transesophageal echocardiogram uses a probe inside the esophagus to create detailed imaging of the heart.
- Transrectal ultrasound uses a probe inserted in the male rectum to analyze the prostate.
- A transvaginal ultrasound scan can analyze the female uterus and ovaries with a probe.
Besides these applications, ultrasound is used to study a lot of other parts of the body. These include the carotid arteries, thyroid gland, blood cells, eyes, pancreas, spleen, liver, and gallbladder. In infants, ultrasound imaging can study the hips, brain, and spine.
Ultrasound scans are also used to analyze the cause of pain or swelling in any general area of the body.
What are the Benefits of Using Ultrasound for Medical Imaging and Diagnosing?
There are more benefits to ultrasound imaging methods than any other medical imaging procedure. Some of the benefits of ultrasound exams are:
- Medical ultrasound is one of the few non-invasive procedures. No needles pierce the body, and no probe goes inside. The entire process takes place externally without insertions.
- There is no pain at all associated with medical ultrasound imaging.
- Methods like X-ray and CT scans have harmful radiation. However, ultrasound energy does not have any such ionizing radiation exposure. It uses sound waves that do not cause any radiation.
- The method is cheap and available everywhere.
- Ultrasound imaging is helpful in the visualization of soft tissues. These tissues do not show in X-rays. It is one of the few methods to analyze blood flow without any insertions in the body.
- Ultrasound is useful for sensitive conditions such as pregnancy, where care is required not to harm the fetus.
- Ultrasound imaging is a real-time imaging method. Real-time images provide faster results, making ultrasound useful for guided needle biopsies and fluid aspiration.
Are There Any Disadvantages of Ultrasound Procedures?
Ultrasound is one of the safest medical examination procedures. There are no known disadvantages or risks associated with this process.
As mentioned earlier, no ionizing radiation is used to create ultrasound images, so there is no threat of medical conditions caused due to radioactivity.
Additionally, being a non-invasive procedure, there is no risk of contamination or pain involved in the process.
How is a Typical Ultrasound Performed?
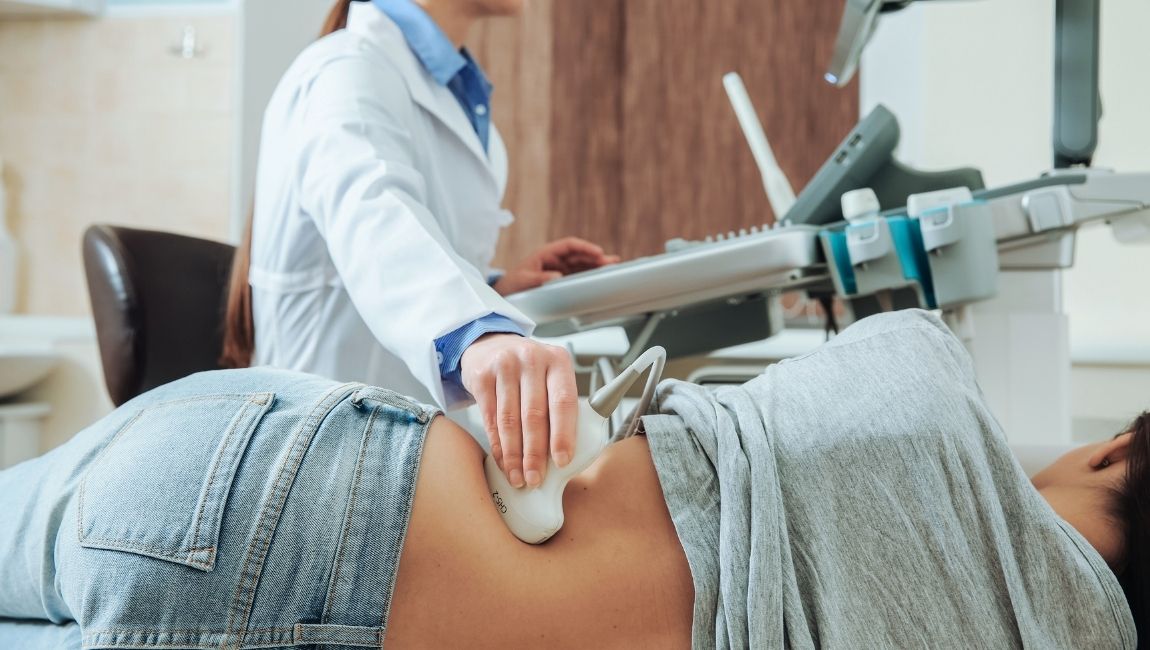
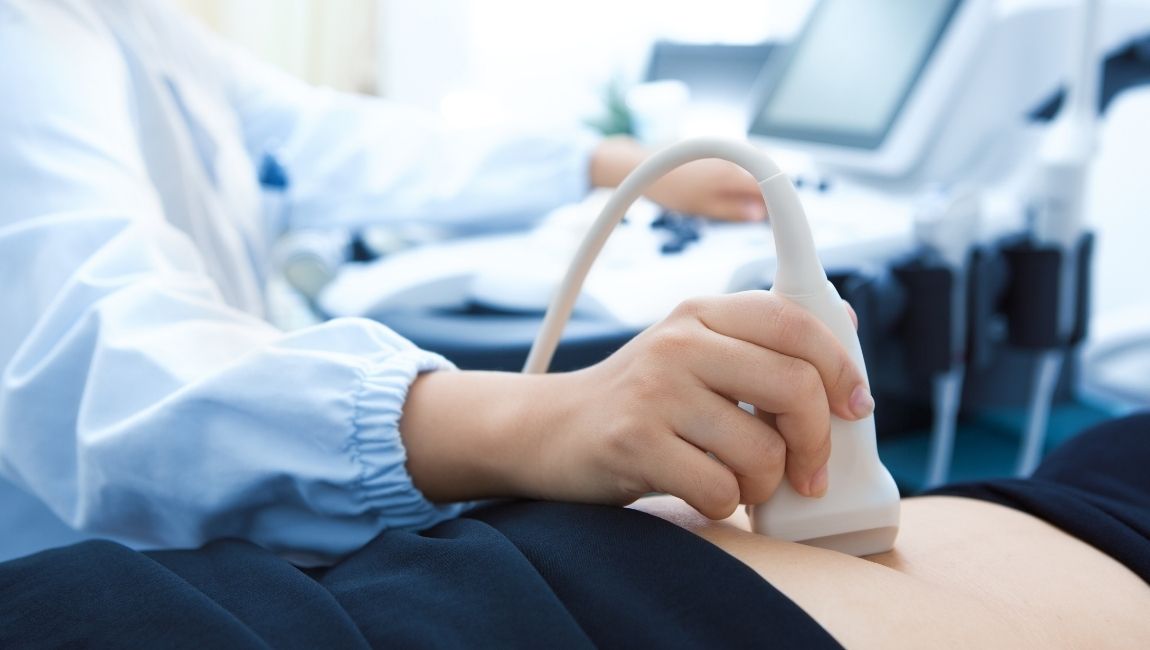
The process of performing a typical ultrasound is simple. The patient lays on an examination table, usually facing upwards. The sonographer adjusts the table and the patient’s position based on the requirements of the particular ultrasound procedure.
Once the patient is in the correct position, the sonographer applies a water-based gel to the area that requires imaging. The gel reduces the air between the transducer and the skin, allowing for better image quality as the sound waves bounce back to the transducer.
Once the gel is applied, the sonographer moves the ultrasound probe around the area of interest. The patient might feel some pressure from the ultrasound probe.
Do patients need to prepare for an ultrasound procedure?
Usually, an ultrasound exam requires minimal special preparation for better image quality and assessment. The doctor or sonographer will provide any preparation guidelines necessary beforehand, based on the area that requires the ultrasound scan.
General instructions for patients undergoing ultrasound exams include:
- Wear loose-fit clothing
- Remove any jewelry or accessories
- In some situations, patients might be asked to wear a hospital gown for the procedure
Doctors commonly ask patients not to eat or drink anything 12 hours before the ultrasound scan. The doctor might also recommend drinking a few glasses of water and avoiding urinating before the ultrasound scan in order to analyze a full bladder.
How Much Do Ultrasound Machines Cost?
The price of ultrasound machines depends on the type of machine you buy and whether you get it new or used. It might surprise you that many of the ultrasound machines you see in a doctor’s office and emergency rooms are refurbished.
Prices of new ultrasound machines start at about $5000 for economical versions and go up to $100,000 and over for flagship models. General ultrasound machines are on the cheaper end, while specialty machines with probes fall on the higher end of the scale.
The price of a used ultrasound machine can vary based on the machine quality and where you obtain it from.
Apart from the price, there are other factors to consider when choosing ultrasound equipment or machine. Some of the most important ones are size, type, portability and image quality.
USC Ultrasound is one of the most reliable suppliers of ultrasound machines and equipment. Many of the machines you see in high-end hospitals or small clinics are sourced from USC Ultrasound.
You can find used and brand-new ultrasound machines at USC Ultrasound. The best part is that if you cannot make a big one-time investment, USC Ultrasound provides financing options.
Endnotes
There are very few medical procedures that come without side effects, risks, or any pain involved. Ultrasound imaging is one of these few.
An ultrasound exam has the ability to map internal tissues and organs in 3D, without necessitating probes and needles. This is why ultrasound machines are present in almost every medical environment.
If you have a clinic or a medical testing facility, getting a good ultrasound machine should be the first thing on your list. Browse through the range available at USC Ultrasound to get the best of these machines and other medical equipment you require.